First Law of motion:
If the net force ( the vector sum of all the forces) is a null vector, the object maintains a uniform rectilinear motion i.e. the velocity of the object is constant.
If the velocity is constant, then the speed and direction are constant since the vector velocity characterizes both the magnitude (speed) and direction.
The first law can thus be mathematically stated as:
We can deduce from the law that:
- If the object is at rest (Net Force = null vector) , it will stay at rest until and unless an external force acts upon it.
- If the motion, it will maintain its movement (uniform rectilinear motion) i.e. with constant velocity until and unless an external force acts upon it.
Second Law of motion:
The Second Law of motion states that the net force (sum of all the forces acting on the object) is equal to the differentiation of its linear momentum by that of time.
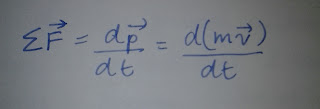 Momentum= mass * velocity
Momentum= mass * velocity
The Second Law can also be stated in terms of acceleration . Since the law works only for constant mass systems, we take the mass out of the differentiation operator.
Using this law, we can say that a body at rest tends to stay at rest until and unless an external force acts on it.
We can also say that an object in motion will maintain a uniform rectillinear motion unless and until an external force acts on it.
We thus proved that the First Law is actually part of the Second Law.
After finding the first Law, Newton took 2 more years to come up with the Second Law (according to some physicists.) what took him so long?
Newton had to invent an essential mathematical tool to make progress in his work: Infinitesimal Calculus. It is said that Issac Newton teamed up with a German Mathematician : Gottreid Leibniz and it is said that these two developed it independently.
If the net force ( the vector sum of all the forces) is a null vector, the object maintains a uniform rectilinear motion i.e. the velocity of the object is constant.
If the velocity is constant, then the speed and direction are constant since the vector velocity characterizes both the magnitude (speed) and direction.
The first law can thus be mathematically stated as:
We can deduce from the law that:
- If the object is at rest (Net Force = null vector) , it will stay at rest until and unless an external force acts upon it.
- If the motion, it will maintain its movement (uniform rectilinear motion) i.e. with constant velocity until and unless an external force acts upon it.
Second Law of motion:
The Second Law of motion states that the net force (sum of all the forces acting on the object) is equal to the differentiation of its linear momentum by that of time.
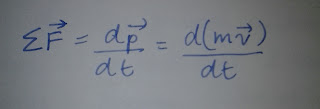 Momentum= mass * velocity
Momentum= mass * velocityThe Second Law can also be stated in terms of acceleration . Since the law works only for constant mass systems, we take the mass out of the differentiation operator.
Using this law, we can say that a body at rest tends to stay at rest until and unless an external force acts on it.
We thus proved that the First Law is actually part of the Second Law.
After finding the first Law, Newton took 2 more years to come up with the Second Law (according to some physicists.) what took him so long?
Newton had to invent an essential mathematical tool to make progress in his work: Infinitesimal Calculus. It is said that Issac Newton teamed up with a German Mathematician : Gottreid Leibniz and it is said that these two developed it independently.




Aucun commentaire:
Enregistrer un commentaire